Student Projects
Student Projects by Associated Institutes
Mid-Range Path Planning Integrating Vision with LLM and Depth Sensing

This project aims to advance the field of robotic navigation by focusing on mid-range path planning, a crucial layer that connects the overarching routes designed by global planning and the immediate, reactive maneuvers of local planning. The project will develop a neural network model capable of generating a sequence of waypoints toward a specified 3D goal position by leveraging current RGB images, GPT cost reasoning from large language model (LLM) , and estimated depth images. This integration will facilitate more efficient navigation through complex environments by smoothing transitions between planning layers and optimizing route adjustments in real-time.
Keywords
Robot Planning; Vision Learning; LLM (Vision GPT) Reason,
Labels
Semester Project , Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-04-26 , Earliest start: 2024-05-01 , Latest end: 2025-01-01
Organization Robotic Systems Lab
Hosts Yang Fan
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Inverse Reinforcement Learning from Expert Pilots

Use Inverse Reinforcement Learning (IRL) to learn reward functions from previous expert drone demonstrations.
Keywords
Inverse Reinforcement Learning, Drones, Robotics
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-04-25 , Earliest start: 2024-05-15 , Latest end: 2025-01-31
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Geles Ismail
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Language-guided Drone Control
Explore the use of large vision language models to control a drone.
Keywords
Human-drone interaction, large language models (LLMs), Robotics
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-04-25 , Earliest start: 2024-05-15 , Latest end: 2025-01-31
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Geles Ismail
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Reinforcement Learning for Drone Maneuvers from Human Preferences

Learn complex drone maneuvers from human feedback using Reinforcement Learning (RL).
Keywords
Reinforcement Learning from human feedback (RLHF), Drones, Robotics
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-04-25 , Earliest start: 2024-05-15 , Latest end: 2025-01-31
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Geles Ismail
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Supporter State Estimation System
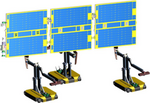
Implementation of a localization and state estimation system for a special ground robot using IMU and 2D LiDAR. The ground robot is part of a Gravity offload system for testing of spacecraft solar arrays (which are designed for microgravity) on earth.
Keywords
State Estimation Localization
Labels
Semester Project
Description
Work Packages
Requirements
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-04-25
Applications limited to ETH Zurich
Organization Autonomous Systems Lab
Hosts Ott Lionel , Pantic Michael
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Master Thesis / Internship: Automated Time Series Analysis in Urinary Tract Assessment in Spinal Cord Injury
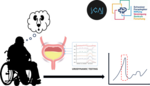
The primary objective of this project is to develop an automated pipeline for the identification and recognition of patterns within urodynamic recordings, utilizing urodynamic recording data in conjunction with annotated patterns provided by experts. This endeavor seeks to reduce the susceptibility of interpreting urodynamic recordings to potential errors arising from human judgment and inaccuracies, thereby improving the management of urinary tract complications in patients with spinal cord injury. By implementing a systematic approach to pattern recognition in Bladder Valomue/Pressure Time Series Measurements of urodynamic data, the potential for error in decision-making can be significantly reduced.
Keywords
Spinal Cord Injury, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Pattern Recognition, Feature Engineering, Time Series Analysis, Signal Processing
Labels
Semester Project , Internship , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-04-21 , Earliest start: 2024-05-19 , Latest end: 2024-12-31
Applications limited to Agroscope , Berner Fachhochschule , CERN , Corporates Switzerland , CSEM - Centre Suisse d'Electronique et Microtechnique , Department of Quantitative Biomedicine , Eawag , Empa , EPFL - Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne , ETH Zurich , Fernfachhochschule , Forschungsinstitut für biologischen Landbau (FiBL) , Friedrich Miescher Institute , Hochschulmedizin Zürich , IBM Research Zurich Lab , Institute for Research in Biomedicine , Lucerne University of Applied Sciences and Arts , NCCR Democracy , NGOs Switzerland , Pädagogische Hochschule St.Gallen , Paul Scherrer Institute , Physikalisch-Meteorologisches Observatorium Davos , Sirm Institute for Regenerative Medicine , Swiss Federal Institute for Forest, Snow and Landscape Research , Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics , Swiss National Science Foundation , SystemsX.ch , Università della Svizzera italiana , Université de Neuchâtel , University of Basel , University of Berne , University of Fribourg , University of Geneva , University of Lausanne , University of Lucerne , University of St. Gallen , University of Zurich , Wyss Translational Center Zurich , Zurich University of Applied Sciences , Zurich University of the Arts , University of Konstanz , Technische Universität München , TU Berlin , Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen , European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) , FH Aachen , Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin , Justus Liebig University, Gießen , Ludwig Maximilians Universiy Munich , Martin Luther Universitat, Halle , Max Delbruck Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) , Max Planck Society , Otto Von Guericke Universitat, Magdeburg , RWTH Aachen University , Social Science Research Center Berlin , Technische Universität Hamburg , TU Darmstadt , TU Dresden , Universität der Bundeswehr München , Universität Ulm , Universität zu Lübeck , University of Cologne , University of Erlangen-Nuremberg , University of Hamburg , Universtity of Bayreuth , Delft University of Technology , Maastricht Science Programme , Radboud University Nijmegen , Utrecht University , Max Planck ETH Center for Learning Systems , European Molecular Biology Laboratory , IEE S.A. Luxembourg , Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia , Technical University of Denmark , Technion - Israel Institute of Technology , University of Southern Denmark , Imperial College London , UCL - University College London , University of Oxford , University of Cambridge , National Institute for Medical Research
Organization Spinal Cord Injury & Artificial Intelligence Lab
Hosts Paez Diego, Dr. , Paez Diego, Dr.
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Development of a smart sock for plantar pressure monitoring
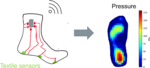
The goal of the project is to develop and test a smart sock prototype for plantar pressure measurements. The smart sock contains textile based pressure sensors and a readout module. This technology can be used for plantar pressure monitoring in diverse wearable applications ranging from healthcare to sports.
Keywords
wearables, smart textiles, plantar pressure, pressure sensors
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-04-16 , Earliest start: 2024-03-01 , Latest end: 2025-02-28
Organization Biomedical and Mobile Health Technology Lab
Hosts Galli Valeria
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Image Based Robust Pose Estimation for General Excavator Buckets

The efficient operation of excavators in construction environments necessitates precise pose estimation of their buckets. Current methods rely on IMUs placed on the excavator arm which require tedious calibration and can be damaged during construction operations. This project aims to leverage computer vision and machine learning to enhance pose estimation, thereby enabling VR overlays for teleoperation and facilitating automation tasks.
Keywords
Computer Vision, Machine Learning, Synthetic Images, Excavators, Construction, 3D Pose Estimation
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Work Packages
Requirements
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-04-16 , Earliest start: 2024-04-01
Organization Robotic Systems Lab
Hosts Schorp Vincent , Terenzi Lorenzo
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Object Slippage Detection for a Miniature Force-Sensitive Gripper

We are developing a teleoperated micro-assembly system. A core component is a force-sensitive micro-gripper. A first gripper prototype has been realized and evaluated. Your task will be to review and improve the current design and to implement automated object slippage detection.
Keywords
Micro-manipulation, robotic gripper, force sensing, slippage detection, teleoperation
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-04-15 , Earliest start: 2023-02-01 , Latest end: 2023-12-31
Organization Bio-Inspired RObots for MEDicine-Laboratory (BIROMED-Lab)
Hosts Duverney Cédric , Rauter Georg, Prof. Dr.-Ing. , Rauter Georg, Prof. Dr.-Ing.
Topics Engineering and Technology
Student Research Assistance for App development in Biosensing and Healthcare Data (~12 months)
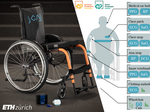
Join a team of scientists improving the long-term prognosis and treatment of Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) through mobile and wearable systems and personalized health monitoring. Joining the SCAI Lab part of the Sensory-Motor Systems Lab at ETH, you will have the unique opportunity of working at one of the largest and most prestigious health providers in Switzerland: Swiss Paraplegic Center (SPZ) in Nottwil (LU).
Keywords
App development, Machine Learning, Data bases, Data engineering, Systems Engineering, Data Modelling
Labels
Internship , Lab Practice , Student Assistant / HiWi , ETH Zurich (ETHZ)
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-04-11 , Earliest start: 2024-06-01 , Latest end: 2025-06-30
Applications limited to ETH Zurich , EPFL - Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne , IBM Research Zurich Lab , Institute for Research in Biomedicine , Hochschulmedizin Zürich , Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics , University of Lucerne , University of Zurich , Zurich University of Applied Sciences , Zurich University of the Arts , Lucerne University of Applied Sciences and Arts , Berner Fachhochschule
Organization Spinal Cord Injury & Artificial Intelligence Lab
Hosts Paez Diego, Dr. , Paez Diego, Dr. , Paez Diego, Dr.
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Learning Robust Agile Flight via Adaptive Curriculum

This project focuses on developing robust reinforcement learning controllers for agile drone navigation using adaptive curricula. Commonly, these controllers are trained with a static, pre-defined curriculum. The goal is to develop a dynamic, adaptive curriculum that evolves online based on the agents' performance to increase the robustness of the controllers.
Keywords
Reinforcement Learning, Drones
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-04-08 , Earliest start: 2023-11-01 , Latest end: 2024-12-31
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Xing Jiaxu
Topics Engineering and Technology
Push Notification Integration for Enhanced Adherence to At-Home Rehabilitation Therapy in Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injury Patients

Adherence to rehabilitation therapy is crucial for the recovery of hand functionality in stroke and traumatic brain injury (TBI) patients. However, sustaining patient motivation to train at home remains a challenge. This project aims to explore the impact of push notifications on adherence to physical therapy among stroke and TBI patients. By investigating the optimal frequency and content of notifications, the goal is to develop a notification/reminder system that fosters continuous engagement with the rehabilitation plan, ultimately promoting increased therapy and better functional outcomes for patients.
Keywords
App Development, Stroke, Traumatic Brain Injury, Rehabilitation, Adherence to Therapy, Push Notifications, mHealth Apps, Interdisciplinary Research, React Native
Labels
Internship , Master Thesis , Student Assistant / HiWi , Summer School
Description
Goal
Tasks
Your Profile
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-04-08 , Earliest start: 2024-04-21 , Latest end: 2025-03-01
Organization Rehabilitation Engineering Lab
Hosts Retevoi Alexandra
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Design & Implementation of Wireless Video Transmission for Endoscopy

In vivo wireless video transmission is cutting-edge but largely unexplored area of research promising to improve a wide variety of minimally-invasive procedures.
Keywords
Wireless video transmission Endoscopy Minimally-invasive procedures Capsule endoscopy Circuit design
Labels
Semester Project , Internship , Master Thesis , Student Assistant / HiWi
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-04-08 , Earliest start: 2024-04-15 , Latest end: 2024-08-31
Organization Multiscale Robotics Lab
Hosts Lyttle Sean
Topics Engineering and Technology
Deep Learning of Residual Physics For Soft Robot Simulation

Incorporating state-of-the-art deep learning approaches to augment conventional soft robotic simulations for a fast, accurate and useful simulation for real soft robots.
Keywords
Soft Robotics, Machine Learning, Physical Modeling, Simulation
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-04-03 , Earliest start: 2024-04-01 , Latest end: 2024-12-31
Organization Soft Robotics Lab
Hosts Michelis Mike , Katzschmann Robert, Prof. Dr.
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Internship/ Master Thesis: Machine Learning for Assessment of Walking Patterns in the SCI population - Time Series Classification

Gait patterns in multiple impairments present unique and complex patterns, which hinders the proper quantitative assessment of the walking ability for chronic ambulatory conditions when translated to daily living. In this project, we will focus on finding clusters of gait patterns through unsupervised learning from a large dataset of incomplete spinal cord injury individuals. The goal is to investigate hidden patterns in relation to the type of injuries and find their application for future diagnosis and rehabilitation treatment. Your work will guide future rehabilitation methods in general clinical practice, through applied classification and dimensionality reduction in Biomechanics of walking. Goal: Develop an unsupervised clustering pipeline for a large dataset of gait patterns from spinal cord injured individuals for class similarity evaluation
Keywords
Medical and health science, computing and computational science, engineering and technology, information, machine learning, data science, data engineering
Labels
Internship , Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis , ETH Zurich (ETHZ)
Project Background
Your Task
Your Benefits
Your Profile
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-04-03 , Earliest start: 2024-06-01 , Latest end: 2025-03-31
Applications limited to EPFL - Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne , ETH Zurich , CERN , Corporates Switzerland , IBM Research Zurich Lab , NGOs Switzerland , Zurich University of Applied Sciences , Wyss Translational Center Zurich , University of Zurich , University of St. Gallen , University of Lucerne , University of Lausanne , University of Geneva , University of Fribourg , University of Berne , University of Basel , Université de Neuchâtel , Università della Svizzera italiana , Swiss National Science Foundation , Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics , Empa , Eawag , TU Berlin , Technische Universität München , Technische Universität Hamburg , RWTH Aachen University , Max Delbruck Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) , Delft University of Technology , UCL - University College London , University of Cambridge , University of Oxford , University of Leeds , University of Manchester , University of Nottingham , National Institute for Medical Research , Imperial College London , Radboud University Nijmegen , Maastricht Science Programme
Organization Sensory-Motor Systems Lab
Hosts Paez Diego, Dr. , Paez Diego, Dr.
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Learning Pose Estimation for Partially Occluded Objects from Simulation

This project addresses the task of 6D pose estimation for general-purpose objects, particularly when dealing with occlusion. We aim to leverage recent deep learning methods and synthetic data generation schemes to enable robust object manipulation.
Keywords
Object Pose Estimation, Perceptive Manipulation, Photorealistic Simulation
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Work Packages
Requirements
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-04-03
Applications limited to ETH Zurich , EPFL - Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne
Organization Robotic Systems Lab
Hosts Zurbrügg René , Bhardwaj Arjun , Patil Vaishakh
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Master Thesis/ Internship: Quantifying Biomechanics of Gait from IMU Data Simulation

Gait analysis is crucial for evaluating walking ability in individuals with ambulatory conditions e.g., Stroke or Parkinson’s disease. Traditional marker-based motion capture systems face limitations in real-life scenarios. This project proposes using wearable IMUs for gait analysis due to their portability. The goal is use datasets already recorded in our labs to model and synchronize IMU data and with 3D motion capture recordings, extract meaningful gait features for different pathologies. The extracted gait features will be validated against, and validate them against a motion capture-based ground truth features calculated for the same patients. This research aims to enhance gait analysis outside of labs and provide valuable insights for decision-making in gait disorders.
Keywords
Gait Analysis, Inertial Measurement Unit, Wearable Sensors, Signal Processing, Pattern Recognition, Machine Learning, Time Series Analysis
Labels
Internship , Master Thesis
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-04-03 , Earliest start: 2024-06-01 , Latest end: 2025-03-31
Applications limited to Agroscope , Berner Fachhochschule , CERN , Corporates Switzerland , CSEM - Centre Suisse d'Electronique et Microtechnique , Department of Quantitative Biomedicine , Eawag , Empa , EPFL - Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne , ETH Zurich , Fernfachhochschule , Forschungsinstitut für biologischen Landbau (FiBL) , Friedrich Miescher Institute , Hochschulmedizin Zürich , IBM Research Zurich Lab , Institute for Research in Biomedicine , Lucerne University of Applied Sciences and Arts , NCCR Democracy , NGOs Switzerland , Pädagogische Hochschule St.Gallen , Paul Scherrer Institute , Physikalisch-Meteorologisches Observatorium Davos , Sirm Institute for Regenerative Medicine , Swiss Federal Institute for Forest, Snow and Landscape Research , Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics , Swiss National Science Foundation , SystemsX.ch , Università della Svizzera italiana , Université de Neuchâtel , University of Basel , University of Berne , University of Fribourg , University of Geneva , University of Lausanne , University of Lucerne , University of St. Gallen , University of Zurich , Wyss Translational Center Zurich , Zurich University of Applied Sciences , Zurich University of the Arts , Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen , European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) , FH Aachen , Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin , Justus Liebig University, Gießen , Ludwig Maximilians Universiy Munich , Martin Luther Universitat, Halle , Max Delbruck Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) , Max Planck Society , Otto Von Guericke Universitat, Magdeburg , RWTH Aachen University , Social Science Research Center Berlin , Technische Universität Hamburg , Technische Universität München , TU Berlin , TU Darmstadt , TU Dresden , Universität der Bundeswehr München , Universität Ulm , Universität zu Lübeck , University of Cologne , University of Erlangen-Nuremberg , University of Hamburg , University of Konstanz , Universtity of Bayreuth , Delft University of Technology , Maastricht Science Programme , Radboud University Nijmegen , Utrecht University , Chalmers University of Technology , Champalimaud Foundation , CNRS - Centre national de la recherche scientifique , European Molecular Biology Laboratory , Grenoble Institute of Technology (G-INP) - Phelma , IDEA League , IEE S.A. Luxembourg , Max Planck ETH Center for Learning Systems , Politecnico di Milano , Research Internships at HU Berlin , Technical University of Denmark , Technion - Israel Institute of Technology , The Microsoft Research – University of Trento Centre for Computational and Systems Biology (COSBI) , Université de Strasbourg , Universiteit Stellenbosch , University College Dublin , University of Southern Denmark , Vienna Biocenter - Scientific Training , Uppsala Universitet
Organization Spinal Cord Injury & Artificial Intelligence Lab
Hosts Paez Diego, Dr.
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Interpretation of instrumented movement analysis in neurorehabilitation

With advancing technology, healthcare professionals now have greater access to quantifying human movement, which will increasingly influence health assessments. However, interpreting movement data, particularly for individuals with neurological impairments, remains challenging. Our project aims to explore experts' insights on interpreting such data. Through multi-center focus groups, we gather healthcare professionals' perspectives to enhance informed decision-making in clinical settings.
Keywords
Neurorehabilitation, Focus Groups, Instrumented Movement Analysis
Labels
Semester Project , Internship
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-04-02 , Earliest start: 2024-04-14 , Latest end: 2024-10-31
Organization Rehabilitation Engineering Lab
Hosts Mayrhuber Laura
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Engineering and Technology , Behavioural and Cognitive Sciences
Exploring Event Generation Strategies

This project focuses on utilizing various techniques for Video to Events generation.
Keywords
Computer Vision, Machine Learning, Event generation, Videos
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-03-26
Applications limited to ETH Zurich , University of Zurich
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Zubic Nikola
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Assessing the feasibility of plantar pressure measurement devices for monitoring the diabetic population
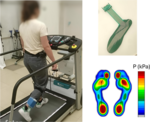
The goal of the project is to assess the feasibility of using commercially available plantar pressure monitoring devices (so called smart insoles) on the diabetic population. Pressure ulcers are a common complication of the diabetic foot, and monitoring plantar pressure continuously is a potential measure of prevention. Diabetic patients are often prescribed personalized footwear (e.g., curved insoles that accommodate any deformity in the feet). This project aims at assessing the potential of the smart insoles available on the market to monitor plantar pressure in diabetic patients with such custom footwear.
Keywords
wearables, mobile health, prevention, plantar pressure monitoring, diabetic foot
Labels
Semester Project , Bachelor Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-03-26 , Earliest start: 2024-04-08 , Latest end: 2024-09-02
Organization Biomedical and Mobile Health Technology Lab
Hosts Galli Valeria
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Lifelike Agility on ANYmal by Learning from Animals

The remarkable agility of animals, characterized by their rapid, fluid movements and precise interaction with their environment, serves as an inspiration for advancements in legged robotics. Recent progress in the field has underscored the potential of learning-based methods for robot control. These methods streamline the development process by optimizing control mechanisms directly from sensory inputs to actuator outputs, often employing deep reinforcement learning (RL) algorithms. By training in simulated environments, these algorithms can develop locomotion skills that are subsequently transferred to physical robots. Although this approach has led to significant achievements in achieving robust locomotion, mimicking the wide range of agile capabilities observed in animals remains a significant challenge. Traditionally, manually crafted controllers have succeeded in replicating complex behaviors, but their development is labor-intensive and demands a high level of expertise in each specific skill. Reinforcement learning offers a promising alternative by potentially reducing the manual labor involved in controller development. However, crafting learning objectives that lead to the desired behaviors in robots also requires considerable expertise, specific to each skill.
Keywords
learning from demonstrations, imitation learning, reinforcement learning
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-03-25
Organization ETH Competence Center - ETH AI Center
Hosts Li Chenhao , Li Chenhao , Klemm Victor
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Learning Real-time Human Motion Tracking on a Humanoid Robot

Humanoid robots, designed to mimic the structure and behavior of humans, have seen significant advancements in kinematics, dynamics, and control systems. Teleoperation of humanoid robots involves complex control strategies to manage bipedal locomotion, balance, and interaction with environments. Research in this area has focused on developing robots that can perform tasks in environments designed for humans, from simple object manipulation to navigating complex terrains. Reinforcement learning has emerged as a powerful method for enabling robots to learn from interactions with their environment, improving their performance over time without explicit programming for every possible scenario. In the context of humanoid robotics and teleoperation, RL can be used to optimize control policies, adapt to new tasks, and improve the efficiency and safety of human-robot interactions. Key challenges include the high dimensionality of the action space, the need for safe exploration, and the transfer of learned skills across different tasks and environments. Integrating human motion tracking with reinforcement learning on humanoid robots represents a cutting-edge area of research. This approach involves using human motion data as input to train RL models, enabling the robot to learn more natural and human-like movements. The goal is to develop systems that can not only replicate human actions in real-time but also adapt and improve their responses over time through learning. Challenges in this area include ensuring real-time performance, dealing with the variability of human motion, and maintaining stability and safety of the humanoid robot.
Keywords
real-time, humanoid, reinforcement learning, representation learning
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-03-25
Organization ETH Competence Center - ETH AI Center
Hosts He Junzhe , Li Chenhao , Li Chenhao
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Continuous Skill Learning with Fourier Latent Dynamics
In recent years, advancements in reinforcement learning have achieved remarkable success in teaching robots discrete motor skills. However, this process often involves intricate reward structuring and extensive hyperparameter adjustments for each new skill, making it a time-consuming and complex endeavor. This project proposes the development of a skill generator operating within a continuous latent space. This innovative approach contrasts with the discrete skill learning methods currently prevalent in the field. By leveraging a continuous latent space, the skill generator aims to produce a diverse range of skills without the need for individualized reward designs and hyperparameter configurations for each skill. This method not only simplifies the skill generation process but also promises to enhance the adaptability and efficiency of skill learning in robotics.
Keywords
representation learning, periodic autoencoders, learning from demonstrations, policy modulating trajectory generators
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-03-25
Organization ETH Competence Center - ETH AI Center
Hosts Li Chenhao , Rudin Nikita
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Universal Humanoid Motion Representations for Expressive Learning-based Control

Recent advances in physically simulated humanoids have broadened their application spectrum, including animation, gaming, augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR), and robotics, showcasing significant enhancements in both performance and practicality. With the advent of motion capture (MoCap) technology and reinforcement learning (RL) techniques, these simulated humanoids are capable of replicating extensive human motion datasets, executing complex animations, and following intricate motion patterns using minimal sensor input. Nevertheless, generating such detailed and naturalistic motions requires meticulous motion data curation and the development of new physics-based policies from the ground up—a process that is not only labor-intensive but also fraught with challenges related to reward system design, dataset curation, and the learning algorithm, which can result in unnatural motions. To circumvent these challenges, researchers have explored the use of latent spaces or skill embeddings derived from pre-trained motion controllers, facilitating their application in hierarchical RL frameworks. This method involves training a low-level policy to generate a representation space from tasks like motion imitation or adversarial learning, which a high-level policy can then navigate to produce latent codes that represent specific motor actions. This approach promotes the reuse of learned motor skills and efficient action space sampling. However, the effectiveness of this strategy is often limited by the scope of the latent space, which is traditionally based on specialized and relatively narrow motion datasets, thus limiting the range of achievable behaviors. An alternative strategy involves employing a low-level controller as a motion imitator, using full-body kinematic motions as high-level control signals. This method is particularly prevalent in motion tracking applications, where supervised learning techniques are applied to paired input data, such as video and kinematic data. For generative tasks without paired data, RL becomes necessary, although kinematic motion presents challenges as a sampling space due to its high dimensionality and the absence of physical constraints. This necessitates the use of kinematic motion latent spaces for generative tasks and highlights the limitations of using purely kinematic signals for tasks requiring interaction with the environment or other agents, where understanding of interaction dynamics is crucial. We would like to extend the idea of creating a low-level controller as a motion imitator to full-body motions from real-time expressive kinematic targets.
Keywords
representation learning, periodic autoencoders
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-03-25
Organization ETH Competence Center - ETH AI Center
Hosts Li Chenhao , Li Chenhao , Li Chenhao
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Humanoid Locomotion Learning and Finetuning from Human Feedback

In the burgeoning field of deep reinforcement learning (RL), agents autonomously develop complex behaviors through a process of trial and error. Yet, the application of RL across various domains faces notable hurdles, particularly in devising appropriate reward functions. Traditional approaches often resort to sparse rewards for simplicity, though these prove inadequate for training efficient agents. Consequently, real-world applications may necessitate elaborate setups, such as employing accelerometers for door interaction detection, thermal imaging for action recognition, or motion capture systems for precise object tracking. Despite these advanced solutions, crafting an ideal reward function remains challenging due to the propensity of RL algorithms to exploit the reward system in unforeseen ways. Agents might fulfill objectives in unexpected manners, highlighting the complexity of encoding desired behaviors, like adherence to social norms, into a reward function. An alternative strategy, imitation learning, circumvents the intricacies of reward engineering by having the agent learn through the emulation of expert behavior. However, acquiring a sufficient number of high-quality demonstrations for this purpose is often impractically costly. Humans, in contrast, learn with remarkable autonomy, benefiting from intermittent guidance from educators who provide tailored feedback based on the learner's progress. This interactive learning model holds promise for artificial agents, offering a customized learning trajectory that mitigates reward exploitation without extensive reward function engineering. The challenge lies in ensuring the feedback process is both manageable for humans and rich enough to be effective. Despite its potential, the implementation of human-in-the-loop (HiL) RL remains limited in practice. Our research endeavors to significantly lessen the human labor involved in HiL learning, leveraging both unsupervised pre-training and preference-based learning to enhance agent development with minimal human intervention.
Keywords
reinforcement learning from human feedback, preference learning
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-03-25
Organization ETH Competence Center - ETH AI Center
Hosts Li Chenhao , Li Chenhao , Chen Xin , Li Chenhao
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Refreshing Articular Cartilage Defects by Laser Ablation - Parameter Optimization and Validation

Cartilage damage in the knee joint can be caused by aging or repetitive actions. It can be treated by surgically removing the damaged cartilage tissue and filling the generated defect with a precisely shaped, healthy cartilage graft. Removing the defected cartilage is commonly done with surgical curettes. We are investigating the use of laser ablation for a more precise defect preparation process. With two different lasers, we managed to obain promising results regarding cell viability in live samples. However, laser parameters such as pulse frequency and energy need to be optimized towards higher cutting efficiency. Your task will be to prepare a setup to test, optimize, and validate various parameter sets using different lasers for articular cartilage ablation.
Keywords
Laser ablation, laser parameter optimization, cartilage regeneration, biomedical engineering
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-03-15 , Earliest start: 2023-02-01 , Latest end: 2023-12-31
Organization Bio-Inspired RObots for MEDicine-Laboratory (BIROMED-Lab)
Hosts Duverney Cédric , Rauter Georg, Prof. Dr.-Ing. , Rauter Georg, Prof. Dr.-Ing.
Topics Engineering and Technology , Physics
gpuFlightmare: High-Performance GPU-Based Physics Simulation and Image Rendering for Flying Robots

gpuFlightmare: High-Performance GPU-Based Physics Simulation and Image Rendering for Flying Robots
Keywords
Reinforcement Learning, Robotics, Simulation, Vision-based Navigation
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-03-14 , Earliest start: 2024-03-13
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Song Yunlong
Topics Engineering and Technology
Using LLMs to adjust to human preferences during human-robot collaboration

We want to exploit LLMs to adjust to human preferences while interacting. We think that we can generate desired behaviors by leveraging LLMs to translate the natural language to robot motion, e.g. "move faster, lift higher, come closer". We aim to carry out tests in a robot-human handover scenario.
Keywords
LLMs, deep learning, human-robot interaction, legged robots
Labels
Master Thesis
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-03-14
Organization Robotic Systems Lab
Hosts Zurbrügg René , Tulbure Andreea
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Behavioural and Cognitive Sciences
Autonomous Flight Using A Camera

Fly like a bird
Keywords
Vision-based Flight, Autonomous Agents, Reinforcement Learning
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-03-14 , Earliest start: 2024-03-13
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Song Yunlong
Topics Engineering and Technology
Visual Representation Learning for Efficient Deep Reinforcement Learning

Visual Representation Learning for Efficient Deep Reinforcement Learning
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-03-14 , Earliest start: 2024-03-13
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Song Yunlong
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Master Thesis/ Internship: Causal Machine Learning with Experts in the Loop for Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) Comorbitities
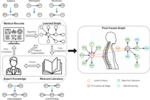
Despite the growing amount of work on applying causal discovery method with expert knowledge to areas of interest, few of them inspect the uncertainty of expert knowledge (what if the expert goes wrong?). This is highly important since that in scientific fields, causal discovery with expert knowledge should be cautious and an approach taking expert uncertainty into account will be more robust to potential bias induced by individuals. Therefore, we aim to develop an iterative causal discovery method with experts in the loop to enable continual interaction and calibration between experts and data. Based on the qualifications of the candidates, we can arrange a subsidy/allowance for covering traveling or living costs.
Keywords
Causal Discovery, Expert Knowledge, Iterative Algorithm, Spinal Cord Injury
Labels
Semester Project , Internship , Master Thesis
Project Background
Your Task
Your Benefits
Your Profile
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-03-13 , Earliest start: 2024-04-15 , Latest end: 2024-10-15
Organization Sensory-Motor Systems Lab
Hosts Paez Diego, Dr. , Paez Diego, Dr.
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Mathematical Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Development of a novel actuator for soft-robotic applications
The Multiscale Robotics Lab develops novel actuation methods for endoscopic devices utilizing magnetic navigation systems. Currently, an external magnetic field can steer permanent magnets through the Euclidean space. Although the gradients of the external magnetic field can be controlled, the actuation of the magnetic continuum robot (m-CR) is still limited. This problem can be overcome by actively re-magnetizing the magnets positioned in the m-CR. The pulse-magnetizer’s driving circuit and magnetization feedback sensors needs to be minimized to fulfill the requirements for medical endoscopic devices.
Keywords
Feedback Control, Actuator Design, Magnetic Hysteresis Modeling, Soft Robotics
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-03-11 , Earliest start: 2024-03-01 , Latest end: 2024-08-31
Organization Multiscale Robotics Lab
Hosts Ehmke Claas
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Deploying Locomotion Policies Trained in Differentiable Simulation on Real Hardware

In recent years, using deep Reinforcement Learning (RL) for robotic motion policies has demonstrated impressive performance, yielding unprecedented robustness on real hardware. Current sim2real approaches rely on large-scale pre-training with domain randomization to make policies robust but struggle with high-dimensional spaces. Current RL methods are primarily limited by their low sample efficiency. Leveraging differentiable simulators for first-order gradient information shows great results for enhancing sample efficiency. Although promising simulation results exist, deployment on hardware is not usually done. The goal of this thesis is to train quadrupedal locomotion policies in a differentiable simulation framework, and then enable real-world deployment by modifying the simulation, the policy training, or the learning algorithm. Ideally, we can leverage properties of differentiable simulators in this process to improve sim2real transfer by fitting real data.
Keywords
Deep Reinforcement Learning, Differentiable Simulation, Quadrupedal Locomotion Control, Sim2Real
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Work Packages
Requirements
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-03-11
Organization Robotic Systems Lab
Hosts Klemm Victor
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Towards AI Safety: Adversarial Attack & Defense on Neural Controllers

The project is collaborating between SRI and RSL/CRL lab and aims to investigate the weakness of the neural controller based on the state-of-the-art [3] attacking method.
Keywords
Adversarial attack; safe AI; Reinforcement learning
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-03-06 , Earliest start: 2024-03-06 , Latest end: 2024-09-30
Applications limited to ETH Zurich , EPFL - Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne
Organization Robotic Systems Lab
Hosts Shi Fan , Shi Fan , Shi Fan
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Physics-informed machine learning in microfluidics
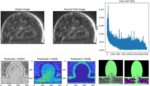
Understanding the distribution and mechanics of velocity and pressure within microaneurysms is crucial for controlling microrobots navigating through them. Traditional methods for velocity and pressure measurement in microchannels, such as particle image velocimetry (PIV) and numerical simulations based on fluidic physics laws, suffer from high computational demands and inability to operate in real-time. Moreover, pure image methods struggle with near-wall regions lacking visible particles. Leveraging recent advancements in machine learning, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs), this project proposes a novel approach - a physics-informed CNN integrated with Navier-Stokes equations and optical flow equations. This CNN aims to accurately predict velocity and pressure profiles in microchannel flows in real-time using only flow images and essential physical parameters. The network architecture comprises an encoder-decoder structure with seven convolutional layers, incorporating down-sampling and up-sampling layers. The final output layer produces three channels representing horizontal velocity, vertical velocity, and pressure. Additionally, a physics-informed loss function, incorporating dimensionless Navier-Stokes equation residuals and optical flow equation residuals, enhances the model's performance by integrating knowledge of fluid dynamics and computer vision. This approach represents a promising advancement towards achieving real-time, high-accuracy prediction of velocity and pressure fields in microchannel flows, with potential applications in microrobotics and microfluidics.
Keywords
artificial Intelligence, physics-informed machine learning, microfluidics, fluid dynamics
Labels
Semester Project , Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-03-05 , Earliest start: 2023-02-09 , Latest end: 2024-09-22
Organization Acoustic Robotics for Life Sciences and Healthcare (ARSL)
Hosts Medany Mahmoud
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology , Physics
Learning Diverse Adversaries to Black-box Learning-based Controller for Quadruped Robots

The project aims to leverage the latest unsupervised skill discovery techniques to validate the state-of-the-art black-box learning-based controllers in diverse ways.
Keywords
Diversity in RL, Trustworthy AI
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-03-02 , Earliest start: 2024-03-02 , Latest end: 2024-08-28
Applications limited to ETH Zurich , [nothing]
Organization Robotic Systems Lab
Hosts Shi Fan , Shi Fan , Shi Fan
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Autonomous Mapping for Construction Site Monitoring

Autonomous mapping systems can provide crucial information for construction monitoring and industrial inspection tasks. They aim to repeatedly map known environments with unknown partial modifications without human intervention.
Keywords
Drone, Computer vision, Path Planning, Mapping
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-29 , Earliest start: 2024-01-01 , Latest end: 2024-07-01
Organization Autonomous Systems Lab
Hosts Pinto Teixeira Lucas
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Towards interpretable learning pipeline: A visual-assisted workflow for locomotion learning

Current reinforcement learning (RL)-based locomotion controllers have shown promising performance. However we are still not clear about what is learned during the training process. In this project, we investigate the proper metrics and visualisation techniques to interactively steer the locomotion learning tasks.
Keywords
Reinforcement learning; visualization; interpretable AI
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-28 , Earliest start: 2024-02-26 , Latest end: 2024-08-26
Organization ETH Competence Center - ETH AI Center
Hosts Zhang Xiaoyu , Shi Fan , Wang April , Shi Fan , Shi Fan
Topics Engineering and Technology
Temporal Graphical Modeling for Understanding and Preventing Autonomic Dysreflexia
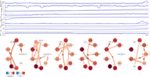
This project will be based on the preliminary results obtained from a previous master project in causal graphical modeling of autonomous dysreflexia (AD). The focus of the extension would be two-fold. One is improving the temporal graphical reconstruction for understanding the mechanism of AD. The other one is building a forecasting framework for the early detection and prevention of AD using the graph structure we constructed before. Please refer to the attached document for more details about the task description. Based on the candidate's qualifications, funding/allowance can be provided.
Keywords
Graphical Modeling; Graph Neural Networks; Multivariate Time Series; Spinal Cord Injuries; Autonomic Dysreflexia; Wearable Sensing
Labels
Semester Project , Internship , Master Thesis , ETH Zurich (ETHZ)
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-28 , Earliest start: 2024-04-01 , Latest end: 2024-10-01
Organization Spinal Cord Injury & Artificial Intelligence Lab
Hosts Paez Diego, Dr. , Li Yanke , Paez Diego, Dr. , Paez Diego, Dr.
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Disease Onset Forecasting through Graphical Modeling Based Digital Twin from Biomedical Data for Spinal Cord Injury Individuals
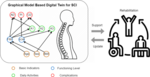
This project focuses on developing an explainable Artificial Intelligence (xAI) framework based on graphical modeling (GM), to enhance the capacity and capability of medical AI. Collaborating with the Swiss Paraplegic Centre (SPZ) for validation, our goal is to improve the long-term prognosis of spinal cord injury (SCI) individuals. Through medical records and a multimodal sensory monitoring system, we aim to create digital twins capable of integrating diverse data sources, guiding medical treatment, and addressing common secondary health conditions in the SCI population. The envisioned GM-based digital twin (GMDT) will represent hierarchical relations across demographic features, functional abilities, daily activities, and health conditions for SCI individuals, allowing for downstream tasks such as prediction, causal inference, and counterfactual reasoning. The assimilation and evolution between the physical and digital twins will be implemented under the GM framework, promising advancements in personalized healthcare strategies and improved outcomes for SCI people. Please refer to the attached document for more details about the task description. Based on the candidate's qualifications, funding/allowance can be provided.
Keywords
Graphical Modelling, Digital Twins, Causal Inference, Data Fusion, Multimodal Learning, Physiological Modelling, Spinal Cord Injuries, Digital Healthcare
Labels
Semester Project , Internship , Master Thesis , ETH Zurich (ETHZ)
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-28 , Earliest start: 2024-03-15 , Latest end: 2024-09-30
Applications limited to TU Dresden , TU Darmstadt , TU Berlin , Technische Universität München , Technische Universität Hamburg , RWTH Aachen University , Max Planck Society , Ludwig Maximilians Universiy Munich , Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin , Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen , Universität zu Lübeck , Imperial College London , UCL - University College London , University of Oxford , University of Cambridge , Delft University of Technology , Zurich University of Applied Sciences , Wyss Translational Center Zurich , University of Zurich , Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics , IBM Research Zurich Lab , ETH Zurich , EPFL - Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne , Empa , Corporates Switzerland , Zurich University of the Arts , University of St. Gallen , University of Lausanne , University of Geneva , University of Fribourg , University of Berne , University of Basel , Swiss National Science Foundation , Swiss Federal Institute for Forest, Snow and Landscape Research , Paul Scherrer Institute , CERN , Department of Quantitative Biomedicine , Eawag , University of Konstanz , University of Cologne , University of Erlangen-Nuremberg , University of Hamburg , Universtity of Bayreuth , Universität Ulm , Universität der Bundeswehr München , Social Science Research Center Berlin , National Institute for Medical Research , Royal College of Art , University of Leeds , University of Manchester , University of Nottingham , University of Aberdeen , Utrecht University , Radboud University Nijmegen , Maastricht Science Programme , Stanford University , Yale University , CNRS - Centre national de la recherche scientifique , Massachusetts Institute of Technology , Max Planck ETH Center for Learning Systems , The University of Tokyo , Tsinghua University , Peking University , Politecnico di Milano , Princeton University , Harvard , University of Toronto , University of Copenhagen , University of California, Berkeley , The University of Edinburgh , Technical University of Denmark , The University of Melbourne , The Australian National University , National University of Singapore , Nanyang Technological University
Organization Spinal Cord Injury & Artificial Intelligence Lab
Hosts Li Yanke , Paez Diego, Dr. , Paez Diego, Dr.
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology , Behavioural and Cognitive Sciences
Microrobot manipulation and ultrasound imaging
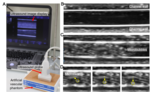
We want to expand the use of acoustic microrobots for biomedical applications by studying their manipulation in 3D environments and their simultaneous real time tracking using non-invasive ultrasound imaging.
Keywords
Microrobots, Ultrasounds, 3D manipulation, Imaging
Labels
Semester Project , Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis , Summer School
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-27 , Earliest start: 2024-01-01 , Latest end: 2024-10-31
Organization Acoustic Robotics for Life Sciences and Healthcare (ARSL)
Hosts Del Alexia
Topics Engineering and Technology
Microrobot manipulation in brain tumor model
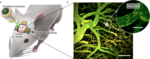
We want to expand the use of acoustic microrobots for drug delivery biomedical applications in brain tumor environments of small mammalian models.
Keywords
Drug delivery, Microrobots, Ultrasounds
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-27 , Earliest start: 2024-01-01 , Latest end: 2024-09-30
Organization Acoustic Robotics for Life Sciences and Healthcare (ARSL)
Hosts Del Alexia
Topics Engineering and Technology , Biology
Acoustic microrobots navigation in tumor vasculature model
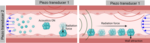
We want to expand the use of acoustic microrobots for drug delivery applications in tumor environments.
Keywords
Microfluidics, drug delivery, Microrobots, Ultrasound, Biomedical
Labels
Semester Project , Collaboration , Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-27 , Earliest start: 2024-02-01 , Latest end: 2024-10-31
Organization Acoustic Robotics for Life Sciences and Healthcare (ARSL)
Hosts Del Alexia
Topics Engineering and Technology
Fabrication of self-growing magnetic micro-catheters
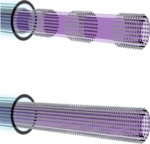
This project aims on the development of a magnetically guidable self-growing micro-catheter.
Keywords
Microrobotics, Self-assembly, Polymers, Nanoparticle
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-27 , Earliest start: 2024-02-28 , Latest end: 2024-04-30
Applications limited to ETH Zurich
Organization Multiscale Robotics Lab
Hosts Hertle Lukas
Topics Engineering and Technology
Mechanophores for advanced wearable strain and pressure sensors
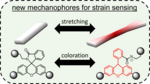
The goal of the project is to synthesize and characterize a number of small molecules capable of acting as mechanophore addition to various polymers. These polymers would then be used as wearable strain or pressure sensors.
Keywords
mechanophore, polymer, wearable, sensor, color, strain, pressure
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-26 , Earliest start: 2023-09-01 , Latest end: 2024-08-01
Organization Biomedical and Mobile Health Technology Lab
Hosts Shokurov Aleksandr
Topics Engineering and Technology , Chemistry
Versatile and Robust Multi-Robot SLAM

Recent work on multi-robot systems with collaborative autonomy has made significant strides towards developing robotic teams capable of performing complex tasks in real, complex settings as shown above. Right at the core of such capabilities is the capability to collaboratively perform SLAM (Simultaneous Localization And Mapping) within such multi-agent systems that can operate efficiently and in challenging real-world environments, which is the main goal of this project. The aim of this project is to develop key components of a multi-robot SLAM system that is robust in challenging environments and adaptable to different scenarios, ranging from environmental monitoring to search-and-rescue operations. The envisioned system will research integrating complementary onboard sensor modalities (e.g., cameras, LiDAR, and IMU), machine learning methods, and distributed communication systems to provide precise localization and mapping exhibiting resilience to sensor failure and sufficient efficiency to be deployed onboard small platforms, such as drones. The student will be guided to work towards a system architecture that can enable effective testing and optimization in state-of-the-art simulation engines, with the ultimate goal of reducing the gap between simulated experiments and real tests. The outlook is to create a system that can be employed onboard a small swarm of drones in a real setting.
Labels
Master Thesis
Work Packages
Requirements
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-21 , Earliest start: 2024-02-01 , Latest end: 2024-10-01
Organization Autonomous Systems Lab
Hosts Pinto Teixeira Lucas
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Aerial Autonomy in Challenging Dynamic Environments

Automating drone navigation promises to revolutionise the way we conduct a wide variety of tasks, such as agricultural monitoring, industrial inspection, and disaster relief scenarios. Equipping a drone with the capability to autonomously explore and map previously unseen environments using onboard sensors and algorithms forms the basis of autonomy. While there has been tremendous progress in this area over the past few years [1-5], existing systems still lack reliability and adaptability to the challenges and complexity of real settings, which is crucial for the deployment of this technology in actual missions. In particular, performing robust navigation and mapping in highly dynamic environments (e.g., forests) remains an open challenge. Following promising leads from the state-of-the-art and our in-house navigation stack, the goal of this project is to develop the capability to deal with increasingly dynamic and complex scenarios. The student will be guided towards leveraging the multi-sensor capabilities of a LiDAR-Visual-Inertial payload being developed in the lab to research approaches for perception and mission planning that can fuse information from the different sensors and capture high-fidelity representations of challenging dynamic environments. Initially, the student will work within a realistic simulation environment and then deploy and test their work onboard a real drone in a real setting.
Labels
Master Thesis
Work Packages
Requirements
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-21 , Earliest start: 2024-02-20 , Latest end: 2024-12-05
Organization Autonomous Systems Lab
Hosts Pinto Teixeira Lucas
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
End-to-end Leaning Terrain Cost with Robot Kinematic Constraints
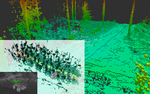
Navigating the unpredictable off-road environment, autonomous robots require a tailored approach to overcome obstacles and optimize pathfinding. Our proposed terrain cost mapping system goes beyond traditional processing by factoring in each robot's specific kinematic abilities. We introduce a novel simulation-based Roll-Out technique to predict a robot's stability over varied terrains, thereby calculating a precise terrain cost. This innovative strategy promises to enhance autonomous navigation by ensuring safe and efficient traversal tailored to individual robotic capabilities.
Keywords
Leaning Terrain Cost; Off-road Navigation; Robot Kinematics
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Work Packages
Requirements
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-21 , Earliest start: 2023-11-30 , Latest end: 2024-01-31
Organization Robotic Systems Lab
Hosts Yang Fan
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Foundation Model for Drone Navigation in Confined Spaces

This master thesis project centers on the development of a foundation model for drone navigation within confined spaces such as ballast tanks of ships.
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-20 , Earliest start: 2024-03-01 , Latest end: 2025-03-01
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Khambhaita Harmish
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Autonomously traversing ship manholes using end-to-end vision-based control

Develop an end-to-end learning-based approach for autonomous drone navigation in ship ballast tank manholes, incorporating both real and simulated training data. The project aims to emphasize speed, a high success rate, and safety in flying through the confined spaces of ship interiors.
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-20 , Earliest start: 2024-03-01 , Latest end: 2025-03-01
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Khambhaita Harmish
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Drone Racing End-to-end policy learning: from features to commands

This project focuses on using RL to learn quadrotor policies to fly at high speeds in complex tracks, directly from features.
Keywords
Robotics, Autonomous Systems, Reinforcement Learning, Quadcopter, Drone Racing
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-20 , Earliest start: 2024-02-19 , Latest end: 2025-12-17
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Romero Angel
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Segmentation and Object Detection in Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) for Enhanced 3D Scene Understanding

This master thesis project focuses on advancing 3D scene understanding through the integration of segmentation and object detection techniques within Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs).
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-20 , Earliest start: 2024-03-01 , Latest end: 2025-03-01
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Khambhaita Harmish
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Vision-Based Autonomous Drone Recovery Using Reinforcement Learning

This project is focused on developing a vision-only flight recovery system for autonomous drones. A critical capability for autonomous drones is to recover safely from any unstable state. This project explores the potential of using reinforcement learning to enable a drone to transition from an unstable to a stable state, using only vision sensors. The challenge lies in creating a system that not only stabilizes the drone but also ensures it can safely land in various unforeseen scenarios.
Keywords
Robotics, Autonomous Systems, Control, Quadcopter
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-20 , Earliest start: 2024-02-19 , Latest end: 2025-07-16
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Romero Angel
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
3D reconstruction of zebrafish larvae based on acoustic rotating
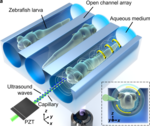
The project is a collaboration between ARSL and CVL. For acoustics, Prof. Daniel will guide you and for AI, Prof. Fisher Yu will guide you. We plan to develop a special 3D reconstruction algorithm for zebrafish larvae. In this project, we first perform the rotation manipulation of zebrafish using an acoustically actuated capillary. Then, we would like to realize the precise 3D reconstruction of the in vivo organs of live zebrafish larvae using CV and AI algorithms. We will fabricate a microchannel chip, which can develop a single polarized vortex. By adjusting the acoustic excitation parameters, we will change the rotational speed and direction. Finally, we will program our special 3D reconstruction algorithms and software.
Keywords
3D reconstruction; AI; CV;Rotation; Micromanipulation; Acoustics;
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-20 , Earliest start: 2024-03-01 , Latest end: 2024-08-31
Organization Acoustic Robotics for Life Sciences and Healthcare (ARSL)
Hosts Ahmed Daniel, Prof.
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology , Biology , Physics
Vision-based Navigation in Dynamic Environment via Reinforcement Learning

In this project, we are going to develop a vision-based reinforcement learning policy for drone navigation in dynamic environments. The policy should adapt to two potentially conflicting navigation objectives: maximizing the visibility of a visual object as a perceptual constraint and obstacle avoidance to ensure safe flight.
Keywords
Reinforcement Learning, Computer Vision, Drones
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-20 , Earliest start: 2023-11-01 , Latest end: 2024-12-31
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Xing Jiaxu
Topics Engineering and Technology
Learning Rapid UAV Exploration with Foundation Models

Recent research has demonstrated significant success in integrating foundational models with robotic systems. In this project, we aim to investigate how these foundational models can enhance the vision-based navigation of UAVs. The drone will utilize learned semantic relationships from extensive world-scale data to actively explore and navigate through unfamiliar environments. While previous research primarily focused on ground-based robots, our project seeks to explore the potential of integrating foundational models with aerial robots to enhance agility and flexibility.
Keywords
Visual Navigation, Foundation Models, Drones
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-20 , Earliest start: 2024-01-25 , Latest end: 2024-12-31
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Xing Jiaxu
Topics Engineering and Technology
Autonomous Drone Navigation via Learning from YouTube Videos

Inspired by how humans learn, this project aims to explore the possibility of learning flight patterns, obstacle avoidance, and navigation strategies by simply watching drone flight videos available on YouTube.
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-19 , Earliest start: 2024-02-19 , Latest end: 2025-02-19
Applications limited to ETH Zurich , University of Zurich
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Cannici Marco
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Gaussian Splatting Visual Odometry

Gaussian Splatting Visual Odometry
Keywords
Computer Vision, Visual Odometry
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-19 , Earliest start: 2024-02-19 , Latest end: 2024-12-01
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Cioffi Giovanni
Topics Engineering and Technology
IMU-centric Odometry for Drone Racing and Beyond

IMU-centric Odometry for Drone Racing and Beyond
Keywords
Computer Vision, Visual-Inertial Odometry, Drone Racing
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-19 , Earliest start: 2024-02-19 , Latest end: 2024-12-01
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Cioffi Giovanni
Topics Engineering and Technology
Navigating on Mars

The first ever Mars helicopter Ingenuity flew over a texture-poor terrain and RANSAC wasn’t able to find inliers: https://spectrum.ieee.org/mars-helicopter-ingenuity-end-mission Navigating the Martian terrain poses significant challenges due to its unique and often featureless landscape, compounded by factors such as dust storms, lack of distinct textures, and extreme environmental conditions. The absence of prominent landmarks and the homogeneity of the surface can severely disrupt optical navigation systems, leading to decreased accuracy in localization and path planning.
Keywords
VIO, SLAM, Computer vision
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-19 , Earliest start: 2024-02-26 , Latest end: 2024-06-30
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Muglikar Manasi
Topics Engineering and Technology
Data-driven Event Generation from Images

In this project, the student applies concepts from current advances in image generation to create artificial events from standard frames. Multiple state-of-the-art deep learning methods will be explored in the scope of this project.
Keywords
Computer Vision, Event Cameras, Deep Learning
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-19 , Earliest start: 2024-02-19
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Messikommer Nico
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Efficient Neural Scene Reconstruction with Event Cameras
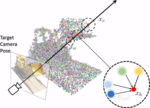
This project seeks to leverage the sparse nature of events to accelerate the training of radiance fields.
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-19 , Earliest start: 2024-02-19 , Latest end: 2025-02-19
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Cannici Marco
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Multimodal Fusion for Enhanced Neural Scene Reconstruction Quality
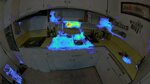
The project aims to explore how prior 3D information can assist in reconstructing fine details in NeRFs and how the help of high-temporal resolution data can enhance modeling in the case of scene and camera motion.
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-19 , Earliest start: 2024-02-19 , Latest end: 2025-02-19
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Cannici Marco
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Domain Transfer between Events and Frames for Motor Policies

The goal of this project is to develop a shared embedding space for events and frames, enabling the training of a motor policy on simulated frames and deployment on real-world event data.
Keywords
Computer Vision, Event Cameras, Robotics, Unsupervised Domain Adaption
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-19 , Earliest start: 2024-02-19
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Messikommer Nico
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Data-driven Keypoint Extractor for Event Data
This project focuses on enhancing camera pose estimation by exploring a data-driven approach to keypoint extraction, leveraging recent advancements in frame-based keypoint extraction techniques.
Keywords
Computer Vision, Event Cameras, Keypoint Extraction, Visual Odometry
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-19 , Earliest start: 2024-02-19
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Messikommer Nico
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
HDR NERF: Neural Scene reconstruction in low light

Implicit scene representations, particularly Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), have significantly advanced scene reconstruction and synthesis, surpassing traditional methods in creating photorealistic renderings from sparse images. However, the potential of integrating these methods with advanced sensor technologies that measure light at the granularity of a photon remains largely unexplored. These sensors, known for their exceptional low-light sensitivity and high dynamic range, could address the limitations of current NeRF implementations in challenging lighting conditions, offering a novel approach to neural-based scene reconstruction.
Keywords
NERF, computer vision, HDR imaging, event camera
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-19 , Earliest start: 2024-02-19 , Latest end: 2024-07-31
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Muglikar Manasi
Topics Engineering and Technology
Low Latency Occlusion-aware Object Tracking

Low latency Occlusion-aware object tracking
Keywords
Computer Vision, Virtual Reality, Object tracking
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-19 , Earliest start: 2024-02-19 , Latest end: 2024-12-01
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Cioffi Giovanni
Topics Engineering and Technology
Event-based occlusion removal

Unwanted camera occlusions, such as debris, dust, raindrops, and snow, can severely degrade the performance of computer-vision systems. Dynamic occlusions are particularly challenging because of the continuously changing pattern. This project aims to leverage the unique capabilities of event-based vision sensors to address the challenge of dynamic occlusions. By improving the reliability and accuracy of vision systems, this work could benefit a wide range of applications, from autonomous driving and drone navigation to environmental monitoring and augmented reality.
Keywords
Event cameras, occlusion, weather, computer vision
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-19 , Earliest start: 2024-02-26 , Latest end: 2024-06-30
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Muglikar Manasi
Topics Engineering and Technology
Foundation Models for Event-based Segmentation

Work on design, implementation, and validation of famous foundation models (CLIP and Segment Anything Model - SAM) in context of Event-based Segmentation.
Keywords
Foundation Models, CLIP, Segment Anything Model, SAM, Event-based Vision, Computer Vision, Object Segmentation, Instance Segmentation, Segmentation, Machine Learning
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-16
Applications limited to ETH Zurich , University of Zurich
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Zubic Nikola
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
What can Large Language Models offer to Event-based Vision?

This project focuses on combining Large Language Models within the area of Event-based Computer Vision.
Keywords
Event-based Vision, Computer Vision, Large Language Models, GPT, Natural Language Processing
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-16
Applications limited to ETH Zurich , University of Zurich
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Zubic Nikola
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
A Fully Integrated Shape-transformable Wearable Ultrasound Helmet
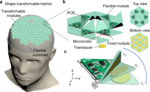
Ultrasound helmets are typically used to focus ultrasound on specific regions of the brain to treat tremors. To date, most ultrasound helmets that have been developed are bulky and rigid, have suboptimal resolution, and produce considerable heat. Ultrasound arrays on flexible sheets offer an exciting new direction, but their application has so far been limited to monitoring. Importantly, no current systems are designed for manipulating microrobots within a 3D vasculature.
Keywords
Wearable, Micro and nanorobots, ultrasound, electronics, brain, acoustics
Labels
Master Thesis , ETH Zurich (ETHZ)
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-15 , Earliest start: 2024-02-15 , Latest end: 2024-12-31
Organization Acoustic Robotics for Life Sciences and Healthcare (ARSL)
Hosts Ahmed Daniel, Prof.
Topics Engineering and Technology
Bioinspired Ultrasound Microrobots
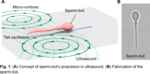
Inspired by naturally-occurring microswimmers such as spermatozoa that exploit the nonslip boundary conditions of a wall, we propose here a microrobot design (a “sperm-bot”) that can execute upstream motility triggered by ultrasound.
Keywords
Robotics, micro and nanorobots, microrobotics, soft robotics ultrasound, bioinspired
Labels
Semester Project , Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis , Summer School
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-15 , Earliest start: 2024-10-01 , Latest end: 2024-12-19
Organization Acoustic Robotics for Life Sciences and Healthcare (ARSL)
Hosts Ahmed Daniel, Prof.
Topics Engineering and Technology
Resonant Acoustic Microrobots
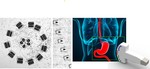
The newly designed microrobot consists of a cavity at the center of its body within the polymer matrix. The microcavity supports an air-bubble trap, which enables propulsion in an acoustic field.
Keywords
Keywords: microrobotics, soft swimmers, acoustics, ultrasound, biomedical applications
Labels
Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-15 , Earliest start: 2024-02-15 , Latest end: 2024-12-19
Organization Acoustic Robotics for Life Sciences and Healthcare (ARSL)
Hosts Ahmed Daniel, Prof.
Topics Engineering and Technology
Embedded algorithms of IMUs in a neurorehabilitation device
The goal of this project is to help develop embedded firmware for a imu based rehabilitation device. This project is part of the SmartVNS project which utilizes movement-gated control of vagus nerve stimulation for stroke rehabilitation.
Keywords
electrical engineering PCB Embedded systems neurorehabilitation
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-14 , Earliest start: 2024-01-06 , Latest end: 2024-12-31
Organization Rehabilitation Engineering Lab
Hosts Donegan Dane , Viskaitis Paulius
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Development of a Clinically Usable Electrode for tVNS

This project aims to develop a clinically usable electrode for transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tVNS) therapy. The objective is to create an electrode that is biocompatible, low-impedance, and easy to use, allowing patients to apply it themselves with minimal setup time. The project involves conducting a literature review, evaluating existing designs, selecting appropriate materials, developing a prototype, and assessing its efficacy and usability in a clinical setting. The outcome will be an electrode that enhances the convenience and effectiveness of tVNS therapy, contributing to improved patient treatment adherence and outcomes.
Keywords
Mechanical engineering, materials engineering, 3D modeling, anatomical modeling, CAD.
Labels
Semester Project , Internship , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Tasks
Your Profile
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-14 , Earliest start: 2023-06-01
Organization Rehabilitation Engineering Lab
Hosts Viskaitis Paulius , Donegan Dane
Topics Engineering and Technology
Activity and fatigue detection using machine learning based on real-world data from smart clothing

The aim of this project is to use machine learning methods to extract useful information such as activity type and fatigue level from real-world data acquired from our textile-based wearable technology during sport activities.
Keywords
smart clothing, wearable technology, textile sensor, fitness tracking, sports medicine, fatigue, machine learning, artificial intelligence, computer science
Labels
Semester Project , Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-14 , Earliest start: 2023-09-15 , Latest end: 2024-05-31
Organization Biomedical and Mobile Health Technology Lab
Hosts Ahmadizadeh Chakaveh
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Multisensory assessment of physiological markers during neural stimulation for stroke rehabilitation

Project goal is to assess outcomes of a non-invasive brain stimulator for future application in stroke rehabilitation. This will involve using an exciting novel method of brain stimulation together with simultaneous multisensory recordings of various physiological parameters, including heart rate, galvanic skin response, pupillometry and electroencephalogram (EEG). The results of the project will help develop brain stimulation protocols that elicit meaningful neural responses in healthy subjects, and in stroke patients.
Keywords
neural stimulation, neural biomarkers, neurophysiology, physiology, neuroscience, EEG, pupillometry
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-14 , Earliest start: 2023-06-01
Organization Rehabilitation Engineering Lab
Hosts Viskaitis Paulius , Donegan Dane
Topics Engineering and Technology
Real-time control of neural stimulation for stroke patients.
Real-time analysis of movement kinematics can benefit multiple different strategies in rehabilitation after stroke, including allowing closed-loop brain stimulation. Use of inertial measurement units (IMUs) allows detection of movement and extraction of kinematic features, but application in real-time remains challenging. This project will develop algorithms for real-time movement data analysis and feature extraction in typical rehabilitation tasks and general real-life movements. In turn, these algorithms will be applied to control novel brain stimulation approaches in stroke neurorehabilitation.
Keywords
Inertial measurement unit, IMU, movement tracking, machine learning, real-time, signal processing
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-14 , Earliest start: 2023-05-09
Organization Rehabilitation Engineering Lab
Hosts Viskaitis Paulius , Donegan Dane
Topics Engineering and Technology
Develop software for wearable technologies
The aim of this project is to develop mobile software to communicate with our already developed textile-based wearable technology and process sensor data for movement monitoring.
Keywords
smart clothing, wearable technology, software development, fitness tracking, sports medicine, mobile application, computer science
Labels
Semester Project , Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-14 , Earliest start: 2023-09-15 , Latest end: 2024-05-31
Organization Biomedical and Mobile Health Technology Lab
Hosts Ahmadizadeh Chakaveh
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Efficient data processing and reporting in stroke neuro-rehabilitation
Project goal is to optimise existing and develop new algorithms into an efficient system for signal pre-processing, data storage, analysis and visualization in motor-neurorehabilitation. This data is generated by stroke patients wearing motion sensors during their therapy sessions. Key endpoint of the project is to display real-time and longitudinal therapy results, which can aid therapists and patients. The results of the project will help develop a more efficient therapy and is a key part of a larger project that seeks to develop an intelligent and closed-loop neural stimulation system for stroke rehabilitation.
Keywords
health biomarkers, data science, computer science, data visualization, data processing, real-time, internet of medical things, IoMT, healthcare internet of things, healthcare IoT
Labels
Semester Project , Internship , Master Thesis
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-14 , Earliest start: 2023-05-09
Organization Rehabilitation Engineering Lab
Hosts Donegan Dane , Viskaitis Paulius
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Design data acquisition solution for smart clothing

The aim of this project is to develop and improve wearable electronics solutions for data acquisition from textile-based sensors used in our smart clothing.
Keywords
smart clothing, wearable technology, textile sensor, fitness tracking, sports medicine, PCB, electronics, computer science
Labels
Semester Project , Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-14 , Earliest start: 2023-09-15 , Latest end: 2024-05-31
Organization Biomedical and Mobile Health Technology Lab
Hosts Ahmadizadeh Chakaveh
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Conduct human gait study with optical motion capture to assess smart clothing for movement monitoring

We aim to conduct a study with human participants to assess the function of our textile-based wearable technology for movement monitoring in clinical and fitness scenarios.
Keywords
smart clothing, wearable technology, textile sensor, fitness tracking, sports medicine, rehabilitation, human study, motion capture, computer science
Labels
Semester Project , Internship , Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-14 , Earliest start: 2023-09-15 , Latest end: 2024-05-31
Organization Biomedical and Mobile Health Technology Lab
Hosts Ahmadizadeh Chakaveh
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Imposition of non-fixed convex constraints on Neural Networks

This project aims to answer the unsolved question of how to guarantee (in a computationally efficient way) hard convex constraints on the output of a network when the parameters that define the constraints change.
Keywords
Neural networks, convex, constraints, hard, optimization
Labels
Semester Project , Collaboration , Master Thesis
Description
Work Packages
Requirements
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-13 , Earliest start: 2024-02-13 , Latest end: 2025-03-29
Organization Robotic Systems Lab
Hosts Tordesillas Jesus
Topics Mathematical Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Advancing Augmented Reality Helmets for motorcyclists and racecars: Independence through Self-Localization
Advancing Augmented Reality Helmets for motorcyclists and racecars: Independence through Self-Localization
Keywords
Localization, Autonomous Driving
Labels
Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-08 , Earliest start: 2024-02-18 , Latest end: 2024-12-01
Organization Robotics and Perception
Hosts Cioffi Giovanni
Topics Engineering and Technology
Controlling a Magnetically Actuated Inverted Pendulum
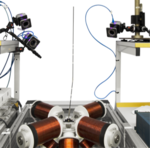
Balancing a 3D inverted pendulum using remote magnetic actuation
Keywords
Inverted Pendulum, Machine Learning, Feedback Control, Dynamical Systems
Labels
Semester Project , Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-08 , Earliest start: 2024-02-11 , Latest end: 2024-09-01
Organization Multiscale Robotics Lab
Hosts Zughaibi Jasan
Topics Engineering and Technology
Why do Parkinson's Patients walk differently?

Investigation of brain activity during walking in Parkinson’s patients
Keywords
Parkinson's disease; EEG; neuroscience; biomechanics; movement;
Labels
Semester Project , Internship , Lab Practice , Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis
PLEASE LOG IN TO SEE DESCRIPTION
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-02 , Earliest start: 2024-03-01 , Latest end: 2024-12-31
Organization Rehabilitation Engineering Lab
Hosts Salzmann Lena, MSc
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Probabilistic Air-ground Localization in Agricultural Environment

Digital environments, or digital twins, allow for design, prototyping, and testing in the virtual world before moving to the real world, thus accelerating development and reducing costs. Digital twin of a farm supports crop operations such as scheduling a harvest or predicting a yield, while agritech companies can develop farm automation robots using a digital twin. The goal of this project is to develop air-ground localization strategies that are capable to be deployed in crop environments during the production season. The main target is to identify individual plants in the ground images using as reference the aerial images.
Keywords
3d Reconstruction, Place Recognition, Aerial Vehicles, Deep Learning, Computer Vision.
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Work Packages
Requirements
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-02 , Earliest start: 2022-08-24 , Latest end: 2023-10-31
Organization Vision for Robotics Lab
Hosts Pinto Teixeira Lucas
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
Long-Term Aerial Localization in Agricultural Environment

Digital environments, or digital twins, allow for design, prototyping, and testing in the virtual world before moving to the real world, thus accelerating development and reducing costs. A digital twin of a farm supports crop operations such as scheduling a harvest or predicting a yield, while agritech companies can develop farm automation robots using a digital twin. The goal of this project is to develop 3D Reconstruction and localization strategies that are capable to identify temporal invariant areas and properties in crop environments during the production season. The main target is to be able to match the same plants over time.
Keywords
3d Reconstruction, Place Recognition, Aerial Vehicles, Deep Learning, Computer Vision.
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Description
Work Packages
Requirements
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-02 , Earliest start: 2023-07-23 , Latest end: 2023-08-31
Organization Autonomous Systems Lab
Hosts Pinto Teixeira Lucas
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
Semantic Segmentation-Aided Bundle Adjustment
Bundle Adjustment (BA) is a critical optimization technique used to refine a visual reconstruction by jointly estimating the 3D scene structure and the viewing parameters. Traditional BA approaches primarily focus on geometric features and might struggle in highly unstructured scenarios, such as natural environments. This project aims to extend the Bundle Adjustment methodology by incorporating higher-level features extracted from semantic segmentation. The integration of semantic information aims to provide contextually relevant and more discriminative data to the adjustment process, thereby improving its accuracy and robustness.
Labels
Semester Project , Master Thesis
Work Packages
Requirements
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-02-02 , Earliest start: 2023-07-30 , Latest end: 2024-05-01
Organization Autonomous Systems Lab
Hosts Pinto Teixeira Lucas , Mascaro Rubén
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
ANYmal Operator meets Mixed Reality

This project aims to build an intuitive mixed reality (MR) interface for robot operators using Apple’s ARKit capabilities. Building on an existing iOS application, we want to provide the operators with a more immersive and informative interface. This involves showing the robot's sensory readings, sketching a global path for it, and playing back the robot's states in the application.
Keywords
ios, app, robotics, augmented reality
Labels
Semester Project , Bachelor Thesis
Description
Work Packages
Requirements
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-01-30 , Earliest start: 2024-02-01
Organization Robotic Systems Lab
Hosts Mittal Mayank
Topics Information, Computing and Communication Sciences
From Pixels to Pulse: How Smartphone Cameras and Machine Learning Illuminate Your Heart's Health

We aim to develop a machine-learning model that assesses heart activity and extract cardiac signal from a smartphone camera.
Keywords
Image processing, time series analysis, biosignal analysis, data science, medical technologies, and digital health.
Labels
Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-01-29 , Earliest start: 2024-02-05 , Latest end: 2025-02-05
Organization Biomedical and Mobile Health Technology Lab
Hosts Elgendi Moe
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Mathematical Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology , Behavioural and Cognitive Sciences , Physics
Analyzing Manual Therapy Forces in Spinal Manipulation

We aim to develop a graphical user interface with an integrated machine learning model to analyze forces applied during manual therapy interventions (spinal manipulation). Data is collected with a flexible sensor matrix between the practitioner and the patient.
Keywords
Time series analysis, force-time profile analysis, data science, and medical technologies
Labels
Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-01-29 , Earliest start: 2024-02-05 , Latest end: 2025-02-05
Organization Biomedical and Mobile Health Technology Lab
Hosts Elgendi Moe
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Mathematical Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology , Behavioural and Cognitive Sciences , Physics
Wearable Insights for Short- and Long-Sleepers

The project aims to develop an affordable wearable system that collects electroencephalograms (EEG) and electrocardiograms (ECG) to identify EEG and ECG features associated with short and long sleepers in a real-world environment.
Keywords
Wearables, sleep stages, brain waves, heart rate, breathing, and body and eye movements during sleep
Labels
Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-01-29 , Earliest start: 2024-02-05 , Latest end: 2024-02-05
Organization Biomedical and Mobile Health Technology Lab
Hosts Elgendi Moe
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Mathematical Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology , Behavioural and Cognitive Sciences , Physics
AI-Powered Heartbeat Tracker with Smartphone Sensing

We aim to develop a machine learning model for accelerometer and camera data collected from a user’s smartphone that can identify the user’s heart rate.
Keywords
Time series analysis, biosignal analysis, data science, medical technologies, and digital health.
Labels
Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-01-29 , Earliest start: 2024-02-05 , Latest end: 2025-02-05
Organization Biomedical and Mobile Health Technology Lab
Hosts Elgendi Moe
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Mathematical Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology , Behavioural and Cognitive Sciences , Physics
Predicting Falls with Smartphone Accelerometers

We aim to develop an Android-based app that utilizes a developed machine learning model and accelerometer data collected via the user’s smartphone for fall detection.
Keywords
Time series analysis, biosignal analysis, data science, medical technologies, and digital health.
Labels
Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-01-29 , Earliest start: 2024-02-05 , Latest end: 2025-02-05
Organization Biomedical and Mobile Health Technology Lab
Hosts Elgendi Moe
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Mathematical Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology , Behavioural and Cognitive Sciences , Physics
Estimating Sweat Biomarker Levels Using Smartphones

Sweat biomarker levels estimation using a smartphone
Keywords
Health Data Science, Biomedical Signal Processing, mHealth, Medical Technologies, and Digital Health
Labels
Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-01-29 , Earliest start: 2024-02-05 , Latest end: 2025-02-05
Organization Biomedical and Mobile Health Technology Lab
Hosts Elgendi Moe
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Mathematical Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology , Behavioural and Cognitive Sciences , Physics
Smartphone Camera for Blood Pressure Classification

Our goal is to develop a smartphone camera-based model capable of distinguishing between hypotensive, normotensive, and hypertensive subjects.
Keywords
Data analytics, image processing analysis, biosignal analysis, data science, medical technologies, and digital health.
Labels
Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-01-29 , Earliest start: 2024-02-05 , Latest end: 2025-02-05
Organization Biomedical and Mobile Health Technology Lab
Hosts Elgendi Moe
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Mathematical Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology , Behavioural and Cognitive Sciences , Physics
Automated Outcome Prediction for Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery

The project aims to develop a predictive model to identify motion features associated with motion improvement in children after surgery.
Keywords
Time-series analysis, biosignal analysis, statistical analysis, biomedical signal processing, and machine learning.
Labels
Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-01-29 , Earliest start: 2024-02-05 , Latest end: 2025-02-05
Organization Biomedical and Mobile Health Technology Lab
Hosts Elgendi Moe
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Mathematical Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology , Behavioural and Cognitive Sciences , Physics
Anxiety Alert: Stay in Control of Your Stress Levels Anywhere, Anytime!

We want to analyze biomedical signals collected from subjects with induced anxiety using a portable device. We aim to detect instantaneous anxiety and mood changes via portable devices. The data were already collected and ready to be analyzed. The data description is here: https://www.mdpi.com/2306-5729/7/9/132
Keywords
Stress detection, biomedical signal analysis, data science, medical technologies, and digital health
Labels
Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis
Description
Goal
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-01-29 , Earliest start: 2024-02-05 , Latest end: 2025-02-05
Organization Biomedical and Mobile Health Technology Lab
Hosts Elgendi Moe
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Mathematical Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology , Behavioural and Cognitive Sciences , Physics
Internships (Industrial or Research) on Body Modelling and Sensing Technology for Health Care in SCI

This hands-on work (internship or semester project) within a clinical setting will bring you close to intelligent health management while exploring multiple data systems. You will experience multimodal data of robotics rehabilitation, general clinical practice, and detailed clinical studies applied in classification and dimensionality reduction.
Keywords
Machine learning, time-series, HR, ECG, BP, wearables, nearables, Medical and health science, healthcare, Android studio, App development
Labels
Semester Project , Internship , Lab Practice , Bachelor Thesis , Master Thesis , Other specific labels , ETH Zurich (ETHZ)
Project Background
Your Task
Your Benefits
Your Profile
Contact Details
More information
Open this project... call_made
Published since: 2024-01-27 , Earliest start: 2023-08-01 , Latest end: 2024-05-31
Applications limited to ETH Zurich , EPFL - Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne , Empa , Eawag , Zurich University of the Arts , Zurich University of Applied Sciences , Wyss Translational Center Zurich , University of Zurich , University of St. Gallen , University of Lucerne , University of Lausanne , University of Geneva , University of Fribourg , University of Berne , University of Basel , Lucerne University of Applied Sciences and Arts , Institute for Research in Biomedicine , IBM Research Zurich Lab , Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics , CSEM - Centre Suisse d'Electronique et Microtechnique , Corporates Switzerland , CERN , Hochschulmedizin Zürich , Université de Neuchâtel , Università della Svizzera italiana , Swiss National Science Foundation , University of Konstanz , University of Hamburg , University of Erlangen-Nuremberg , University of Cologne , Universität zu Lübeck , Universität Ulm , Universität der Bundeswehr München , TU Dresden , TU Darmstadt , TU Berlin , Technische Universität Hamburg , Max Planck Society , Otto Von Guericke Universitat, Magdeburg , RWTH Aachen University , Ludwig Maximilians Universiy Munich , Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin , European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) , Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen , Max Delbruck Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) , Technische Universität München , Imperial College London , National Institute for Medical Research , Royal College of Art , UCL - University College London , University of Aberdeen , University of Cambridge , University of Manchester , University of Nottingham , University of Oxford , University of Leeds , Delft University of Technology , Maastricht Science Programme , Radboud University Nijmegen , Utrecht University
Organization Sensory-Motor Systems Lab
Hosts Paez Diego, Dr. , Paez Diego, Dr. , Paez Diego, Dr.
Topics Medical and Health Sciences , Information, Computing and Communication Sciences , Engineering and Technology
